

What Is the Use of 24C02? A Practical Guide to AT24C02 EEPROM
In embedded electronics, memory defines behavior. Fast memory enables performance. Non-volatile memory enables persistence. The AT24C02 EEPROM exists squarely in the second category—and that is precisely why it still matters.
Despite its small size, the 24C02 quietly powers millions of devices worldwide. It stores the data that must not disappear. Settings. Calibration. Identity. In this guide, we explore what the AT24C02 is, what it is used for, and why it remains relevant in modern designs.
“Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication.” — Leonardo da Vinci
The 24C02 embodies this principle perfectly.
What Is AT24C02 EEPROM?
The AT24C02 is a 2-kilobit (256-byte) serial EEPROM that communicates over the I²C bus. EEPROM stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory. Unlike RAM, it retains data when power is removed.
Definition and Basic Working Principle
AT24C02 stores data in floating-gate memory cells. Data is written electrically and retained for years without power. Reads are fast. Writes are slower but reliable.
What “24C02” Means
- 24 → I²C serial EEPROM family
- C → CMOS technology
- 02 → 2 kilobits (Kb) total capacity
That equals 256 bytes, organized as 32 pages × 8 bytes.
Why AT24C02 Is Still Widely Used
Newer memories exist. Larger ones too. Yet AT24C02 persists because it is:
- Cheap
- Proven
- Vendor-agnostic
- Easy to integrate
What Is the Use of 24C02?
The core use of the 24C02 is data persistence.
Why Non-Volatile Memory Is Needed
Systems reboot. Power fails. Batteries die. But some data must survive:
- User preferences
- Calibration constants
- Product identity
EEPROM ensures continuity.
RAM vs MCU Flash vs External EEPROM
| Memory Type | Volatile | Typical Use | Write Endurance |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAM | Yes | Runtime variables | Unlimited |
| MCU Flash | No | Firmware | ~10⁴–10⁵ |
| AT24C02 EEPROM | No | Settings & IDs | ~10⁶ |
Typical Roles of AT24C02
- Store configuration parameters
- Preserve factory calibration
- Hold serial numbers and MAC addresses
- Maintain counters and flags
What Data Is Commonly Stored in a 24C02?
The 24C02 is small—but strategic.
Common Data Types
- Device settings: thresholds, modes, preferences
- Calibration values: sensor offsets, gains
- Unique identifiers: serial numbers, product codes
- Counters: power-on count, error count
- Firmware parameters: preserved across updates
This is low-frequency, high-importance data.
Core Features and Specifications of AT24C02
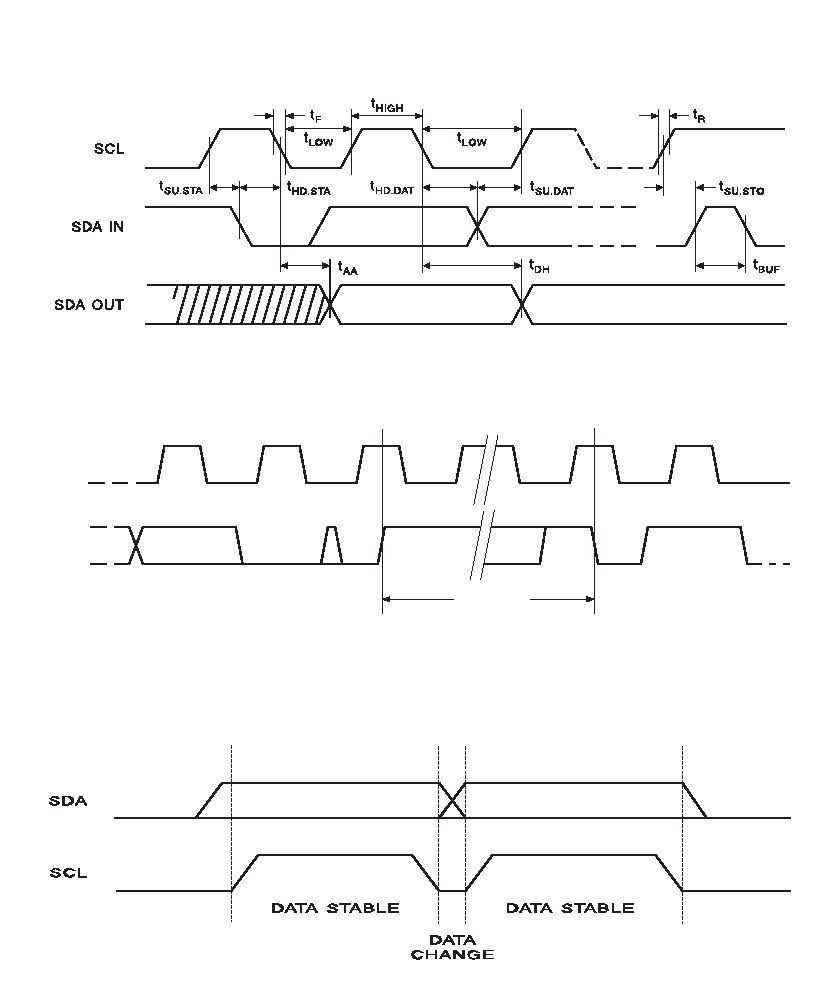
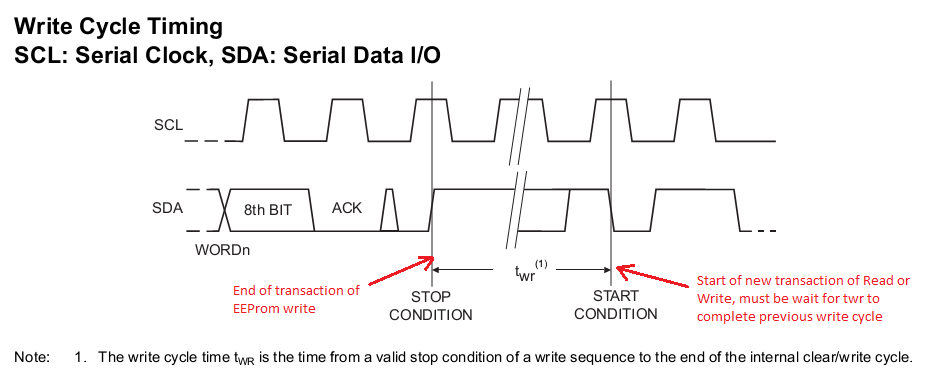
Understanding the specs helps prevent misuse.
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Memory Size | 2 Kb (256 bytes) |
| Interface | I²C |
| Page Size | 8 bytes |
| Write Cycle Time | ~5 ms |
| Endurance | 1,000,000 writes |
| Data Retention | 40–100 years |
| Voltage Range | 1.8V – 5.5V (variant dependent) |
Reliability Matters
EEPROM trades speed for longevity and safety. That tradeoff is intentional.
How AT24C02 Works in an Embedded System
I²C Communication Basics
AT24C02 uses SDA and SCL lines. Device selection occurs via:
- Fixed base address (0x50)
- Hardware pins A0–A2
Up to 8 devices can share one bus.
Read and Write Flow
- Master sends start condition
- Sends device address
- Sends memory address
- Reads or writes data
- Sends stop condition
Page Write Behavior
Writes are limited to 8 bytes per page. Crossing a page boundary causes data wrap—an easy mistake for beginners.
Power-Loss Considerations
Power loss during a write can corrupt data. Best practice:
- Use checksums
- Delay writes until power is stable
AT24C02 Pinout and Hardware Design
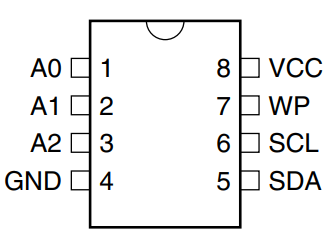

Pin Functions
- SDA / SCL – I²C data and clock
- A0–A2 – Address selection
- WP – Write Protect
- VCC / GND – Power
Write Protect (WP)
Tie WP high to prevent accidental writes. This is critical in safety or industrial systems.
Pull-Up Resistors
I²C requires pull-ups. Typical values:
- 4.7kΩ for short lines
- 2.2kΩ for faster buses
Programming and MCU Compatibility
AT24C02 works with nearly every MCU.
Popular Platforms
- Arduino
- STM32
- PIC, AVR, ESP32, NXP, Renesas
Software Support
Most platforms offer:
- Blocking read/write APIs
- EEPROM abstraction layers
- Mature libraries
Multiple Devices on One Bus
Use A0–A2 pins to assign unique addresses. Simple. Scalable.
Typical Applications of AT24C02
Where It Shines
- Consumer electronics (routers, appliances)
- Industrial controllers
- Automotive modules
- Medical devices
- Battery-powered IoT nodes
In all cases, data integrity matters more than speed.
Advantages and Limitations of AT24C02
Advantages
- Simple interface
- Low cost
- High endurance
- Multi-vendor sourcing
- Long lifecycle support
Limitations
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| Small size | Not for logs |
| Slow writes | Not real-time |
| Wear | Avoid frequent writes |
AT24C02 vs Alternatives
| Memory Type | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| MCU EEPROM | Integrated | Limited size |
| Flash | High density | Low endurance |
| FRAM | Fast & durable | Higher cost |
| AT24C02 | Balanced | Small capacity |
Rule of thumb:
If you need a few hundred bytes that must never be lost, 24C02 is ideal.
Data Safety and Best Practices
- Enable WP when possible
- Avoid unnecessary writes
- Use wear-leveling for counters
- Add CRC or checksum
Good design extends EEPROM life by decades.
Is AT24C02 the Right Choice for Your Project?
Choose AT24C02 when:
- Data size ≤ 256 bytes
- Write frequency is low
- Cost and reliability matter
Choose alternatives when:
- Logging is frequent
- Data size grows
- Write speed is critical
Frequently Asked Questions About 24C02
How much data can it store?
256 bytes.
How many write cycles?
About 1 million per byte.
Can it replace Flash?
No. Different purposes.
Is it still relevant?
Absolutely. Simpler systems demand proven solutions.
Final Thought
The AT24C02 is not glamorous. It is not fast. It is not large.
But it is trustworthy.
In embedded systems, trust is everything.
