What Is the Difference Between MAX13487 and MAX485?
RS-485 has survived decades of industrial change for one simple reason: it works when everything else fails.
But not all RS-485 transceivers are created equal.
The MAX485 is a classic. Cheap. Simple. Everywhere.
The MAX13487 is modern. Hardened. Built for punishment.
They serve the same protocol—but very different engineering eras.
This guide cuts through datasheets and marketing claims. It explains the real differences that matter in design, reliability, and long-term cost.
Overview of RS-485 Communication
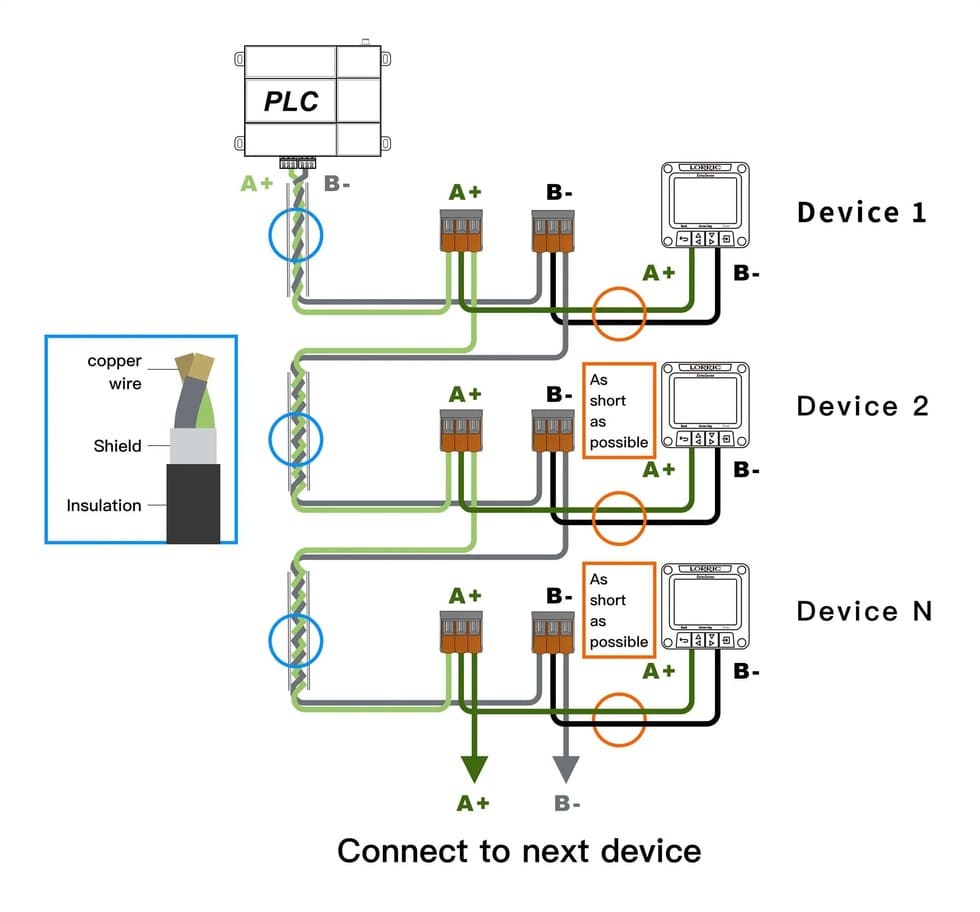

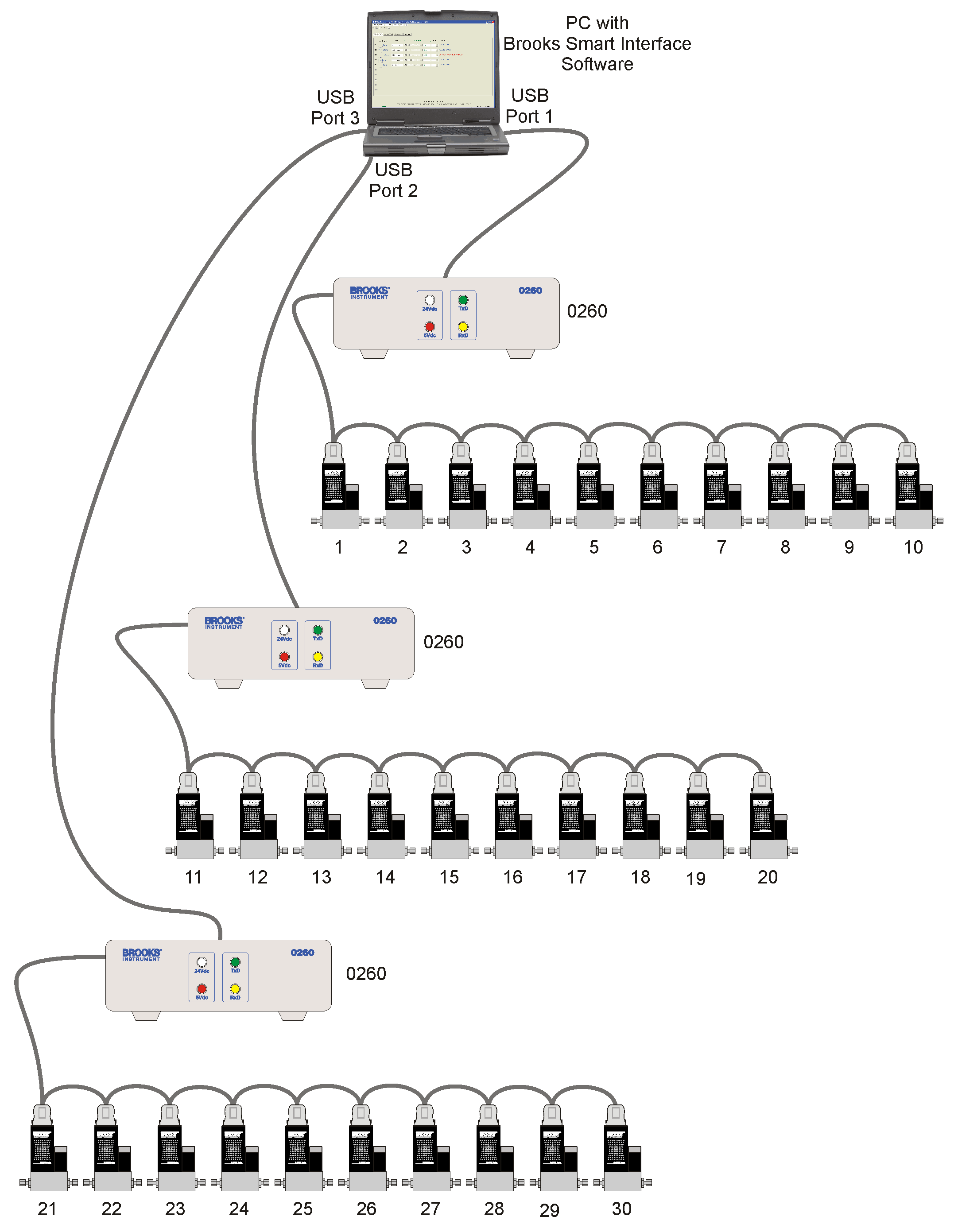
RS-485 is not a protocol.
It is a physical layer standard that defines how bits move across wires.
Why RS-485 Is Widely Used
- Differential signaling rejects noise
- Long cable runs (up to 1200 m)
- Multi-drop support (many devices on one bus)
- Low cost and simple wiring
This makes RS-485 ideal for industrial control, building automation, and energy systems.
“In noisy environments, differential signaling is not optional—it is survival.” — Industrial Design Handbook
RS-485 vs RS-422 (Short Clarification)
- RS-422: point-to-point or multi-drop receivers only
- RS-485: true multi-drop, bidirectional bus
Half-Duplex Reality
Most RS-485 systems are half-duplex:
- One driver active at a time
- Direction control handled by the transceiver
This is where transceiver behavior becomes critical.
Introduction to MAX485

The MAX485 is the default RS-485 chip in textbooks, kits, and low-cost designs.
Design Intent
It was created when:
- Boards were simple
- Noise was manageable
- Protection was external
Key Characteristics
| Feature | MAX485 |
|---|---|
| Data rate | Up to 2.5 Mbps |
| Supply voltage | 5 V only |
| ESD protection | Minimal |
| Fail-safe | External biasing required |
| Package | DIP, SOIC |
Why It Became Popular
- Extremely cheap
- Easy to understand
- Widely cloned
- Massive ecosystem support
Limitations
- No integrated protection
- Sensitive to ground shifts
- Vulnerable to hot-plug damage
- Unsafe in harsh environments
MAX485 works—until it doesn’t.
Introduction to MAX13487

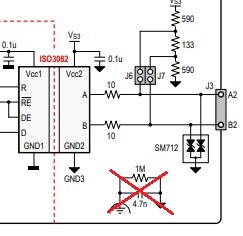
The MAX13487 represents a new generation of RS-485 transceivers.
It assumes:
- Mis-wiring will happen
- Ground offsets are unavoidable
- Hot-plugging is normal
- EMI is aggressive
Design Goals
- Industrial robustness
- Built-in protection
- Safe behavior under fault
Electrical Overview
| Feature | MAX13487 |
|---|---|
| Data rate | Up to 500 kbps |
| Supply voltage | 3.3 V to 5 V |
| ESD protection | ±15 kV |
| Fail-safe | Integrated |
| Temperature | −40°C to +125°C |
Integrated Protection
- Short-circuit tolerant
- Bus fault protection
- Thermal shutdown
- Idle-bus fail-safe receiver
Typical Environments
- PLC I/O modules
- Smart meters
- Factory automation
- Outdoor control systems
MAX13487 is designed for failure—and survives it.
Key Differences Between MAX13487 and MAX485
This is the core comparison engineers care about.
Electrical and Functional Comparison
| Category | MAX485 | MAX13487 |
|---|---|---|
| Era | Legacy | Modern industrial |
| Data rate | Higher | Lower |
| Voltage | 5 V only | 3.3–5 V |
| Fail-safe | External | Internal |
| ESD | Weak | Very strong |
| Fault tolerance | Minimal | Extensive |
| Hot-plug | Unsafe | Safe |
Ground Shift Tolerance
- MAX485: easily damaged
- MAX13487: designed for ± ground offsets
EMI and Signal Integrity
MAX13487 uses controlled edge rates to reduce:
- EMI emissions
- Reflections on long cables
This improves compliance and stability.
Power-Up, Hot-Plug, and Fault Behavior
This section separates lab designs from field-ready systems.
MAX485 Risks
- Undefined bus state at power-up
- Driver contention during startup
- Lock-up if powered mid-bus
MAX13487 Advantages
- Predictable bus behavior
- Safe high-impedance on fault
- No latch-up during hot insertion
“The cost of one truck roll dwarfs the cost of a better transceiver.” — Industrial Maintenance Principle
If your device can be plugged in while powered—MAX485 is a liability.
Design and Application Considerations
When MAX485 Makes Sense
- Short cables
- Clean lab environment
- Hobby projects
- Cost-critical consumer designs
When MAX13487 Is the Better Choice
- Long cables
- Outdoor installations
- Industrial cabinets
- Regulatory compliance needed
Layout and Biasing
- MAX485 requires external bias resistors
- MAX13487 simplifies BOM and layout
Drop-In Replacement Warning
Pin compatibility ≠ behavioral compatibility.
Always validate:
- Timing
- Direction control
- Idle bus behavior
Real-World Application Examples
| Application | Recommended Part | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| PLC backplane | MAX13487 | Noise + hot-plug |
| Modbus RTU | MAX13487 | Bus stability |
| HVAC controller | MAX13487 | Long cables |
| Arduino project | MAX485 | Cost |
| Smart meter | MAX13487 | Compliance |
Industrial systems punish weak designs.
Buying, Migration, and Final Recommendation
Can MAX13487 Replace MAX485?
Electrically? Often yes.
Behaviorally? Not always.
Review:
- Enable timing
- Bus idle state
- Fail-safe assumptions
Cost vs Reliability
- MAX485: lower unit price
- MAX13487: lower lifetime cost
The Final Verdict
| Choose If You Need | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Cheapest RS-485 | MAX485 |
| Industrial reliability | MAX13487 |
| Compliance + uptime | MAX13487 |
| Learning or prototyping | MAX485 |
Summary: Legacy Simplicity vs Modern Robustness
MAX485 is a classic tool.
MAX13487 is a field-ready solution.
One assumes perfection.
The other assumes chaos.
And real-world systems always choose the part that survives chaos.
If you want, I can also:
- Provide a migration checklist
- Create a design decision flowchart
- Compare MAX13487 vs newer alternatives
Just tell me.
