IS62WV25616BLL Arduino Wiring: Complete Guide for Parallel SRAM Integration


External SRAM looks intimidating.
Wide buses. Many wires. Tight timing.
But once you understand the logic, it becomes predictable, powerful, and fast.
This guide explains how to wire and use the IS62WV25616BLL parallel SRAM with Arduino boards.
It is written for hardware-focused makers, embedded developers, and retro-computing enthusiasts who need real memory bandwidth, not slow serial storage.
“Fast memory is not optional. It defines what your system can become.” — Embedded Systems Design Principle
Understanding IS62WV25616BLL SRAM Basics
Static RAM (SRAM) stores data as long as power is present.
No refresh cycles. No erase delays. No wear limits.
The IS62WV25616BLL is a high-speed, low-power parallel SRAM designed for microcontrollers, DSPs, and display buffers.
Unlike EEPROM or SPI RAM, SRAM behaves like true system memory.
When External SRAM Is Needed
Arduino’s internal memory is limited:
| Board | SRAM |
|---|---|
| Arduino Uno | 2 KB |
| Arduino Mega | 8 KB |
| Arduino Due | 96 KB |
That fills up fast.
You need external SRAM when you work with:
- Frame buffers for TFT or VGA displays
- Audio or sensor data buffering
- Retro game emulation
- Large lookup tables
- High-speed logging before SD writes
SRAM shines when speed matters more than persistence.
Core Specifications Explained
The IS62WV25616BLL follows a 32K × 16-bit organization.
That equals 512 Kbits (64 KB) of ultra-fast memory.
Key Electrical Specs
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Memory size | 512 Kbit |
| Organization | 32K × 16 |
| Supply voltage | 3.3 V |
| Access time | 8–10 ns (grade dependent) |
| Standby current | Very low (CMOS) |
Short sentence.
Big impact.
This chip is orders of magnitude faster than I²C or SPI memory.
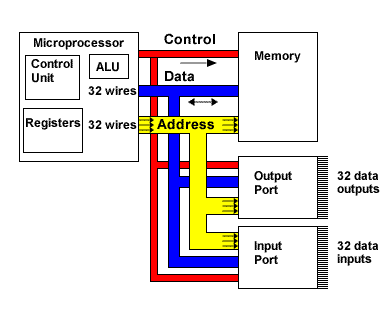
Pinout and Electrical Characteristics
Parallel SRAM uses three signal groups.
Address Bus, Data Bus, Control Signals
| Signal Type | Pins |
|---|---|
| Address | A0–A14 |
| Data | D0–D15 |
| Control | CE, OE, WE |
That is 32 pins of logic, plus power and ground.
Control Pins Explained
- CE (Chip Enable)
Activates the chip. HIGH = disabled. - OE (Output Enable)
Controls read output drivers. - WE (Write Enable)
LOW during write cycles.
Correct timing is critical.
Wrong order = corrupted data.
“Digital systems fail silently. Timing is truth.”
Arduino Compatibility and Hardware Planning
Not all Arduino boards are equal.
Choosing the Right Arduino Board
For this SRAM, pin count matters more than clock speed.
| Board | Verdict |
|---|---|
| Arduino Uno | ❌ Not recommended |
| Arduino Mega | ✅ Best choice |
| Arduino Due | ⚠️ Advanced users only |
The Arduino Mega offers enough GPIO pins for:
- 15 address lines
- 16 data lines
- 3 control lines
Logic Level Compatibility
The SRAM is 3.3 V only.
Options:
- Use 3.3 V Arduino (Due, some ARM boards)
- Add level shifters
- Use series resistors for protection (not ideal)
Never connect 5 V logic directly.
Required Supporting Components
Bare wiring is risky.
Support parts stabilize signals and protect the chip.
Essential Components
- 0.1 µF decoupling capacitors (close to VCC pins)
- Bulk capacitor (1–10 µF nearby)
- Optional pull-ups on control lines
- Optional bus transceiver (74HC245)
Clean power = stable memory.
IS62WV25616BLL Arduino Wiring and Bus Design
Parallel buses need discipline.
Address Bus Wiring Strategy
- Connect A0–A14 directly to Arduino pins
- Keep wires short and parallel
- Avoid breadboards for final builds
Data Bus Direction Control
Data lines must switch direction:
- Write: Arduino → SRAM
- Read: SRAM → Arduino
You control direction by OE and WE timing.
Control Signal Wiring
| Signal | Arduino Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CE | Digital pin | Active LOW |
| OE | Digital pin | Active LOW |
| WE | Digital pin | Active LOW |
Never assert OE and WE at the same time.
That causes bus contention.
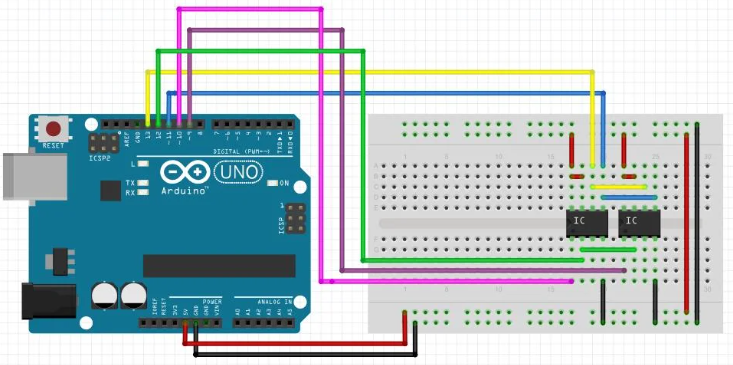
Practical Wiring Example (Arduino Mega)
Below is a simplified mapping example.
Example Pin Mapping Table
| SRAM Pin | Arduino Mega |
|---|---|
| A0–A14 | D22–D36 |
| D0–D15 | D37–D52 |
| CE | D53 |
| OE | D51 |
| WE | D50 |


Common Wiring Mistakes
- Swapped address lines
- Floating OE or WE pins
- Long jumper wires
- Missing decoupling capacitors
SRAM does not forgive sloppy wiring.
Arduino Code for IS62WV25616BLL
Code is simple.
Timing is everything.
Basic Write Cycle Logic
- Set address
- Set data pins as OUTPUT
- Assert CE LOW
- Pulse WE LOW
- Release WE, then CE
Basic Read Cycle Logic
- Set address
- Set data pins as INPUT
- Assert CE LOW
- Assert OE LOW
- Read data
- Release OE, then CE
Avoid digitalWrite() in performance-critical loops.
Use direct port manipulation for speed.
| Method | Speed |
|---|---|
| digitalWrite | Slow |
| Direct PORT | Fast |
| Inline ASM | Fastest |
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
Parallel SRAM is about throughput.
How to Go Faster
- Group address pins on same PORT
- Use bit masks
- Disable interrupts during access
- Match timing to datasheet limits
Signal Integrity Tips
- Short traces
- Ground plane if possible
- Avoid ribbon cables
- Use series resistors for ringing
“Most memory bugs are electrical, not logical.”
Real-World Applications
This chip unlocks serious projects.


Where IS62WV25616BLL Excels
- TFT or VGA frame buffers
- Oscilloscope-style data capture
- Audio sample buffering
- Z80 / 6502 emulation
- External heap for complex firmware
When SRAM Is Not the Right Choice
- Long-term storage → EEPROM or Flash
- Low-pin-count designs → SPI RAM
- Ultra-low power → FRAM
Choose the right memory for the job.
Comparison With Alternatives
| Memory Type | Speed | Pins | Persistence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel SRAM | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | High | No |
| SPI RAM | ⭐⭐ | Low | No |
| I²C EEPROM | ⭐ | Very Low | Yes |
| Flash | ⭐⭐ | Medium | Yes |
Parallel SRAM is raw power.
Final Thoughts
Wiring the IS62WV25616BLL looks complex.
But complexity buys capability.
Once connected correctly, it behaves like real system memory.
Fast. Predictable. Powerful.
If you need speed, determinism, and control, this chip delivers.
If you want next:
- Ready-to-paste Arduino Mega SRAM driver
- Optimized port-level access code
- Timing-diagram–based write macros
- Or a comparison hub linking SRAM vs EEPROM vs SPI RAM
Just say the word 👍
