Introduction to Raspberry Pi and STM32
The debate between Raspberry Pi and STM32 is sharp and persistent.
One feels like a tiny computer.
The other behaves like a disciplined brain.
Both are powerful.
Both are popular.
Yet they serve very different purposes.
As the proverb attributed to Albert Einstein reminds us: “Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not simpler.”
Choosing the wrong platform complicates everything.
Let’s break it down—clearly, calmly, and completely.
What is Raspberry Pi?
Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer (SBC).
It runs full operating systems like Linux.
It supports multitasking, networking, displays, and storage.
Think of it as a mini PC—small, flexible, and user-friendly.
What is STM32?
STM32 is a family of microcontrollers produced by STMicroelectronics.
It does not run a full OS by default.
Instead, it executes bare-metal or real-time code with extreme precision.
STM32 is built for control, not convenience.
Comparing Raspberry Pi and STM32: Key Differences
| Feature | Raspberry Pi | STM32 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Single-board computer | Microcontroller |
| OS | Linux-based | Bare metal / RTOS |
| Power Usage | High | Very low |
| Real-time Control | Limited | Excellent |
| Boot Time | Seconds | Milliseconds |
Performance and Processing Power

Performance is not just speed.
It is predictability, latency, and control.
Raspberry Pi CPU Capabilities
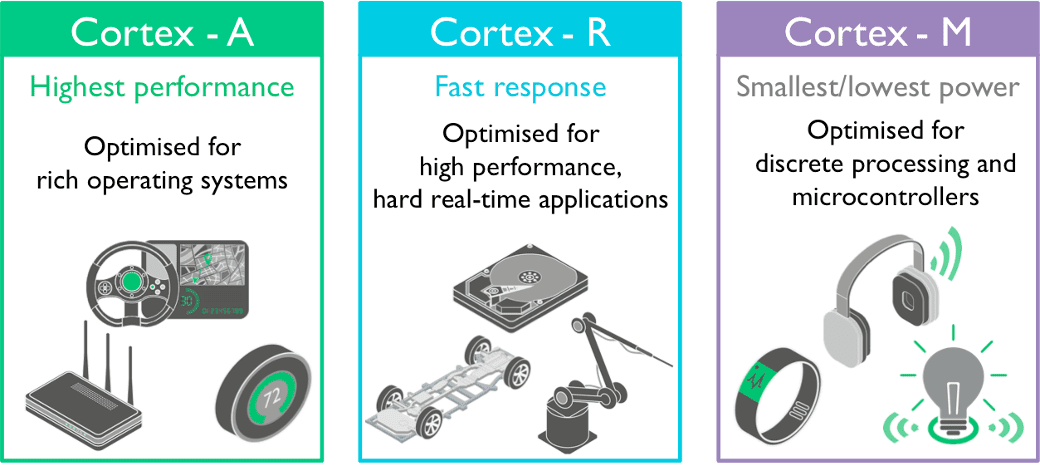
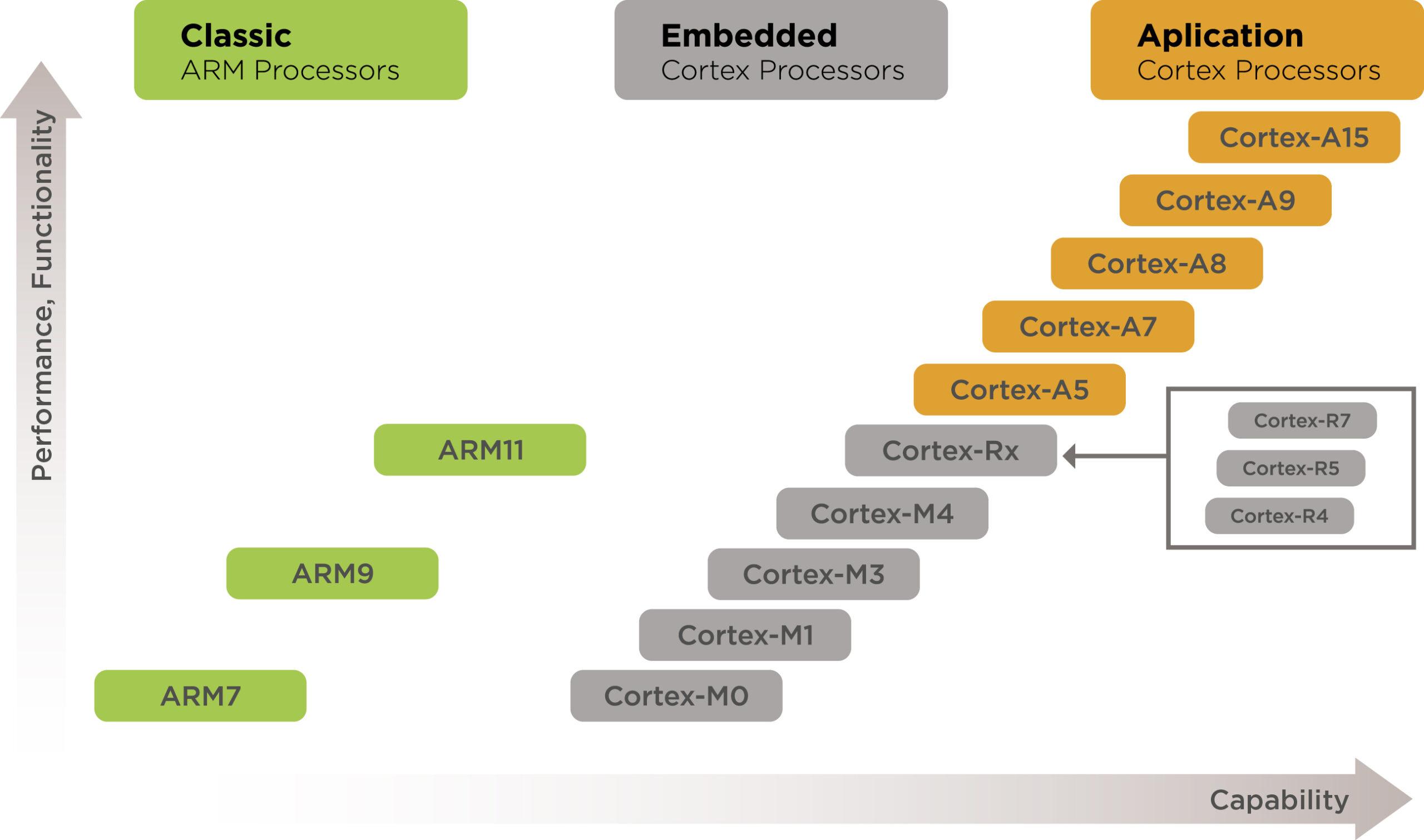
Raspberry Pi uses ARM Cortex-A processors.
These CPUs are designed for:
- Multitasking
- Multimedia
- Networking
- Desktop-like workloads
They shine in data-heavy and UI-driven tasks.
STM32 CPU Capabilities
STM32 uses ARM Cortex-M cores.
These processors focus on:
- Deterministic timing
- Interrupt handling
- Hardware control
They sacrifice raw speed for absolute reliability.
Comparing ARM Cortex-M3 vs ARM Cortex-A Series
| Aspect | Cortex-M (STM32) | Cortex-A (Raspberry Pi) |
|---|---|---|
| Clock Speed | Lower | Higher |
| Real-Time Response | Excellent | Limited |
| Power Draw | Minimal | Significant |
| OS Support | RTOS / Bare metal | Full Linux |
Speed wins headlines.
Precision wins products.
Power Consumption and Efficiency

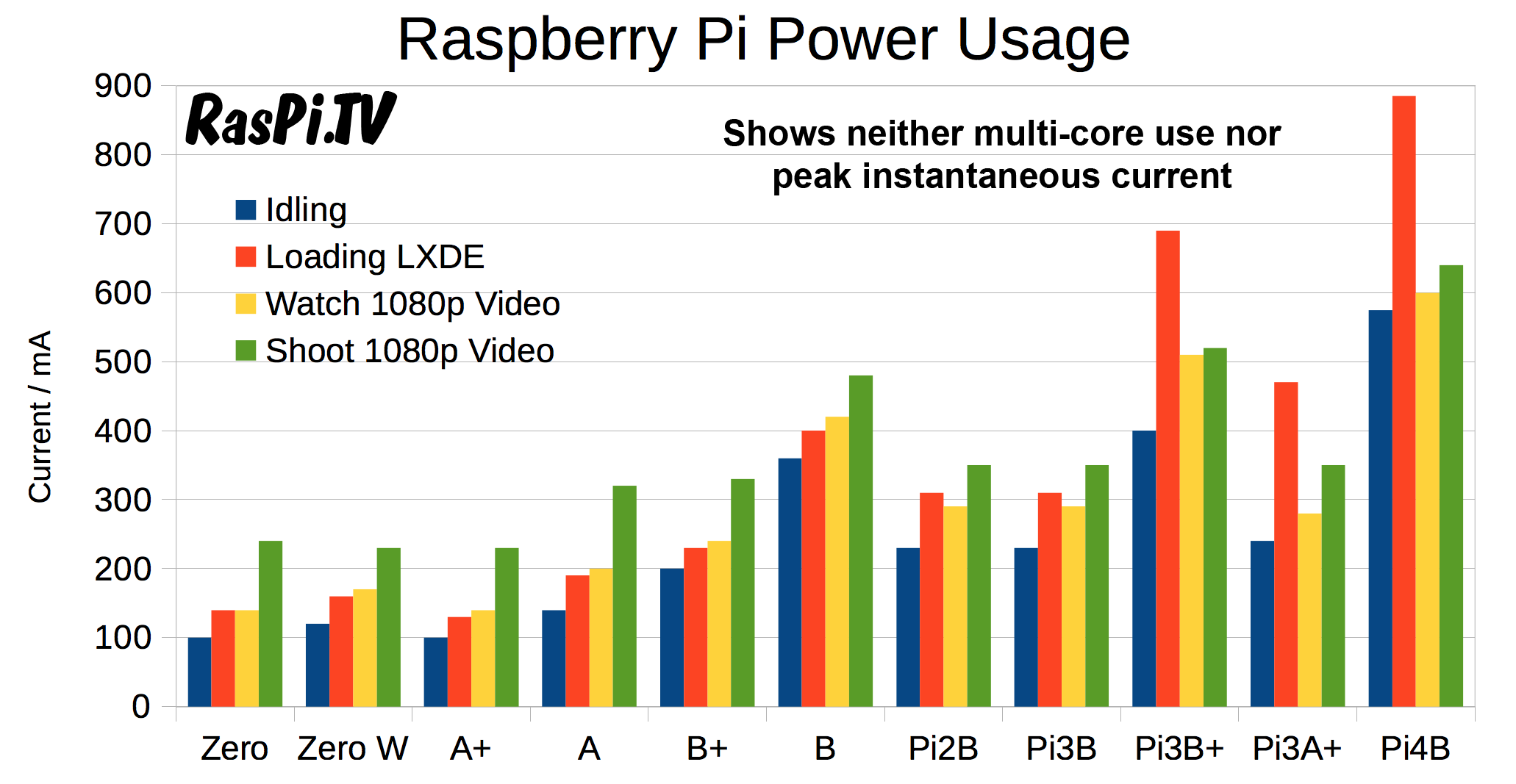

Power is often the silent deal-breaker.
Power Requirements for Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi typically consumes 300–1000 mA.
It needs:
- Stable power
- Proper shutdown
- Heat management
Battery-powered designs struggle here.
Power Efficiency of STM32
STM32 can run on microamps.
Sleep modes extend battery life from days to years.
This makes STM32 ideal for:
- IoT sensors
- Wearables
- Industrial monitoring
When to Choose Low Power Consumption
If your device must sleep, wake, and survive, STM32 wins.
If power is abundant and features matter more, Raspberry Pi fits.
As engineers say: “Power saved is performance earned.”
Programming and Development Environment


Development speed shapes adoption.
Raspberry Pi Development Tools and Languages
Raspberry Pi supports:
- Python
- C/C++
- Java
- Node.js
Linux tools are familiar and forgiving.
Beginners feel productive fast.
STM32 Development Tools (CubeIDE, CubeMX)
STM32 relies on:
- STM32CubeIDE
- STM32CubeMX
- Embedded C/C++
The learning curve is steeper.
But control is absolute.
Ease of Use Comparison
| Factor | Raspberry Pi | STM32 |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Gentle | Steep |
| Debugging | Software-based | Hardware-focused |
| Control Precision | Moderate | Exceptional |
Ease favors Raspberry Pi.
Mastery favors STM32.
Connectivity and Communication Interfaces

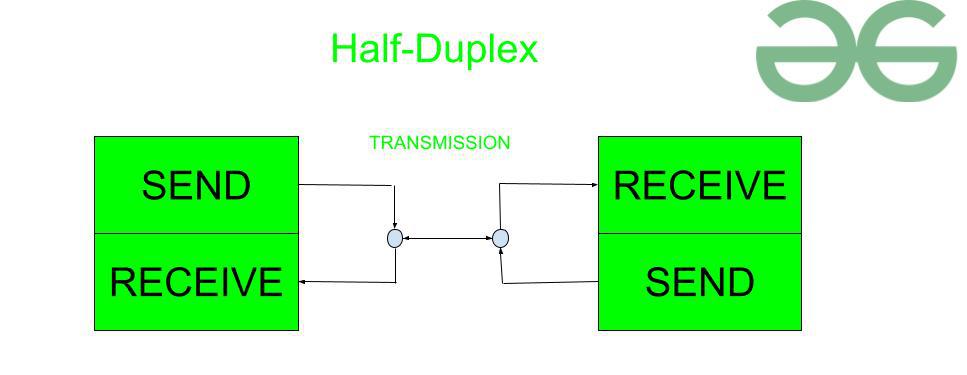
Communication defines usefulness.
Raspberry Pi Communication Options
Raspberry Pi offers built-in:
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- Ethernet
- USB
It connects to the world instantly.
STM32 Communication Options
STM32 provides industrial-grade interfaces:
- UART / USART
- SPI
- I2C
- CAN
- Modbus
Perfect for machines, not browsers.
Which Platform Offers Better Connectivity?
Raspberry Pi wins in consumer networking.
STM32 dominates industrial and real-time communication.
Different worlds.
Different rules.
Applications and Use Cases


Use cases reveal truth.
Popular Raspberry Pi Projects
- Media centers
- Home automation hubs
- AI prototypes
- Web servers
It thrives in experimentation and education.
Popular STM32 Applications
- Motor controllers
- Medical devices
- Automotive ECUs
- Smart sensors
It lives in products that must not fail.
Choosing the Right Platform
| Scenario | Best Choice |
|---|---|
| Desktop-like tasks | Raspberry Pi |
| Real-time control | STM32 |
| Battery operation | STM32 |
| Rapid prototyping | Raspberry Pi |
Cost and Availability


Cost is more than price.
Price Comparison
- Raspberry Pi: higher upfront cost
- STM32: cheaper per unit
At scale, STM32 becomes far more economical.
Availability and Ecosystem
Raspberry Pi shortages have been real.
STM32 chips are widely distributed across vendors.
Ecosystem maturity favors STM32 in industry.
Budget-Based Choice
Small volume + fast results → Raspberry Pi
Mass production + efficiency → STM32
Conclusion: Is Raspberry Pi Better than STM32?




Summary of Key Differences
Raspberry Pi is versatile and friendly.
STM32 is precise and efficient.
One is not better.
One is more appropriate.
Final Recommendation Based on Use Case
Choose Raspberry Pi if you need:
- Linux
- Networking
- Fast development
Choose STM32 if you need:
- Real-time control
- Low power
- Production reliability
As the engineering proverb goes:
“The right tool disappears in use.”
Choose wisely—and your design will speak for itself.
